Subject to annual renewal, the term of a standard patent (R) lasts for a maximum of 20 years from the date of filing of the designated patent application.
In order to keep a standard patent (R) in force up to its maximum term of 20 years, you are required to pay the first renewal fee which is due on the fourth anniversary date of filing of the designated patent application following the date of grant of a standard patent (R). The subsequent renewal payment falls due on every anniversary date thereafter until the expiry of the 20-year patent protection term.
You can pay the renewal fee up to 3 months before the due date. You can still renew the patent within a 6-month grace period after the due date but an additional late fee will be incurred.
Here are two hypothetical examples—
Example 1: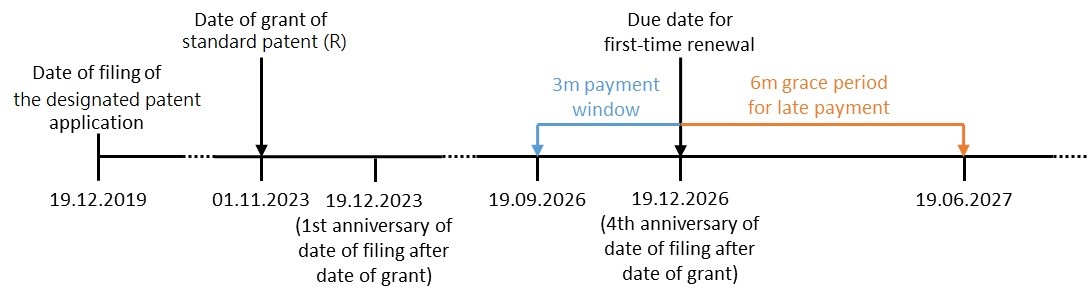
Example 2: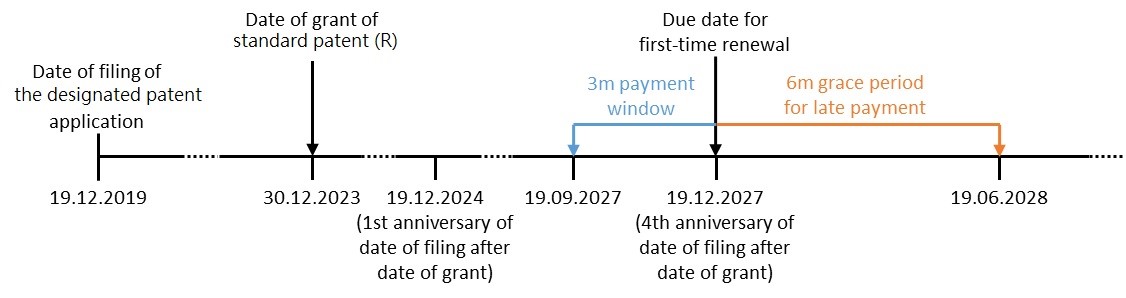
Note: A time limit that expires on a day which is not a business day shall be extended to the next business day.